TensorFlow Lite Converter เป็นตัวแปลงโมเดล TensorFlow ตัวเต็ม ให้ย่อลงมาเป็นโมเดลขนาดเล็ก ที่ทำงานได้รวดเร็ว สำหรับรันกับ Interpreter บนอุปกรณ์ Edge Device ที่มี Resource จำกัด ด้วยเทคนิค Quantization โดยพิจารณาจาก Hardware ปลายทาง ที่จะนำโมเดลไป Deploy เช่น อุปกรณ์ IoT Device, มือถือ Mobile, Microcontroller ต่าง ๆ
TensorFlow Lite Converter คืออะไร
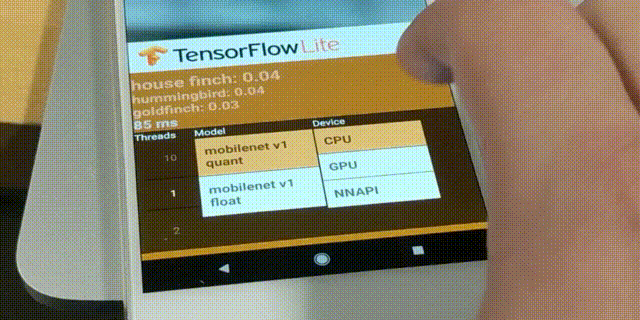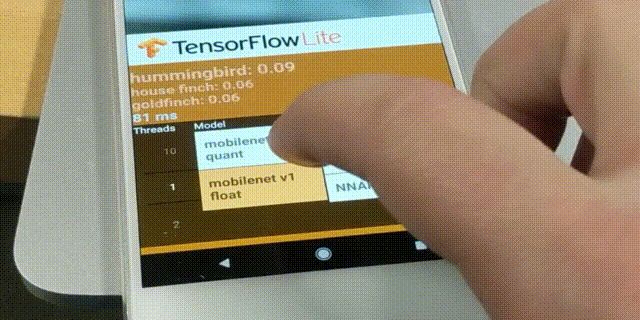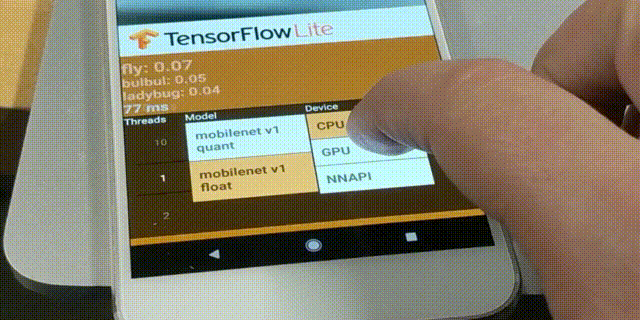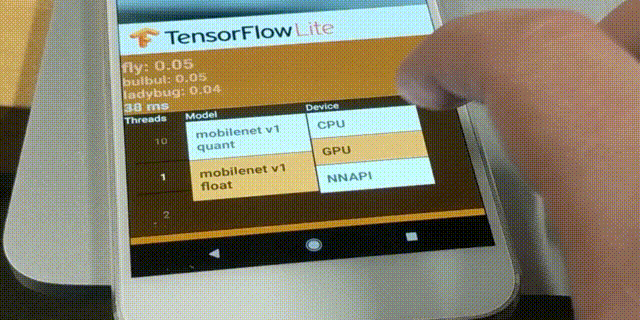
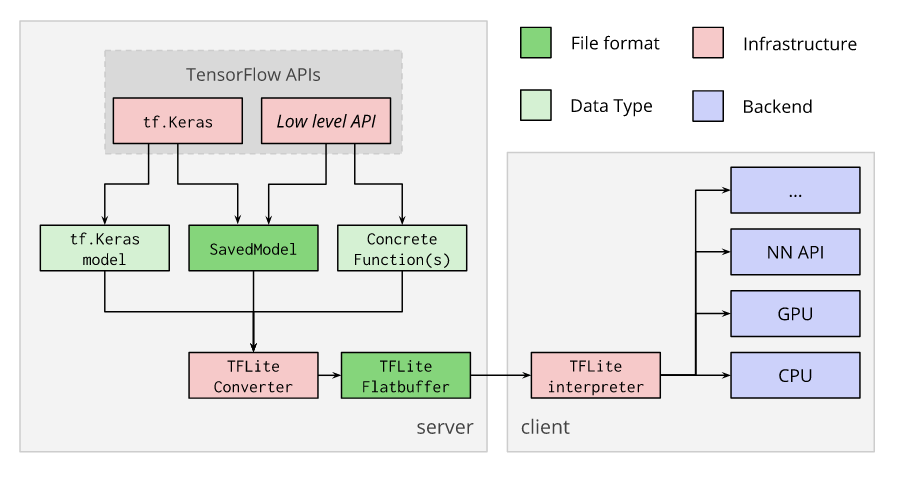
TensorFlow Lite Converter จะแปลงโมเดล TensorFlow ไปเป็นไฟล์ TensorFlow Lite FlatBuffer (ไฟล์นามสกุล .tflite) โดยรองรับโมเดลต้นทางในรูปแบบ SavedModel, tf.keras, และ Concrete Function
เราจะนำไฟล์ FlatBuffer ของ TensorFlow Lite ไป Deploy บนอุปกรณ์ที่ต้องการ แล้วรันด้วย TensorFlow Lite Inteprter สำหรับ Platform นั้น ๆ ดังกระบวนการด้านล่าง
Converting models
เราควรเรียกใช้ TensorFlow Lite Converter ด้วย Python API จากภายในโปรแกรม ซึ่งจะทำการแปลงโมเดลทำได้ง่าย และเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ Model Deveopment Pipeline
การใช้ Python API มีข้อดีคือช่วยให้เรารู้ปัญหาเรื่อง Compatibility แต่เนิ่น ๆ ลดปัญหาในระยะยาว
และนอกจากนี้ เรายังสามารถใช้ Command Line Tools ในการ Convert โมเดลที่ไม่ซับซ้อนมากได้